m ((username removed) (log details removed): Text replacement - "ES:" to "") |
(Changed categories.) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<bookshelf src="Book: | <bookshelf src="Book:Advanced editing" /> | ||
A "Magic word" is a string of text that is recognized by the knowledge base. It triggers the software to return the value of a function, such as dates, website statistics or page names. | |||
==Types of Magic words== | |||
There are basically four different types of Magic words: | There are basically four different types of Magic words: | ||
*'''[[ | *'''[[Magic words#Behavior switch|Behavior switch]]''' (or "Double underscore"): <code><nowiki>__TOC__</nowiki></code> | ||
*'''[[ | *'''[[Magic words#Variable|Variable]]''': <code><nowiki>{{FULLPAGENAME}}</nowiki></code> | ||
*'''[[ | *'''[[Magic words#Tag|Tag]]''': <code><nowiki><gallery></nowiki></code> | ||
*'''[[ | *'''[[Magic words#Parser function|Parser function]]''': <code><nowiki>{{#ifeq:x|y|true|false}}</nowiki></code> | ||
===Behavior switch=== | ===Behavior switch=== | ||
'''Characteristics of a behavior switch''' | '''Characteristics of a behavior switch''' | ||
| Line 34: | Line 29: | ||
'''Characteristics of a tag''' | '''Characteristics of a tag''' | ||
* '''Purpose:''' often used for custom development to process dynamic content | *'''Purpose:''' often used for custom development to process dynamic content | ||
* '''Syntax''': <code><nowiki><smartlist /></nowiki></code> | * '''Syntax''': <code><nowiki><smartlist /></nowiki></code> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 41: | ||
*'''Syntax:''' <code>'''<nowiki>{{#if:</nowiki>'''<nowiki>{{{field|}}}</nowiki> | <nowiki>{{{field|}}}</nowiki> | N/A '''<nowiki>}}</nowiki>'''</code> | *'''Syntax:''' <code>'''<nowiki>{{#if:</nowiki>'''<nowiki>{{{field|}}}</nowiki> | <nowiki>{{{field|}}}</nowiki> | N/A '''<nowiki>}}</nowiki>'''</code> | ||
'''Description''' | '''Description''' | ||
Parser functions are similar to variables, but take one or more parameters.Example:<syntaxhighlight lang="php"> | Parser functions are similar to variables, but take one or more parameters.Example:<syntaxhighlight lang="php"> | ||
{{#ifeq:{{{type}}}|warning | {{#ifeq:{{{type}}}|warning | ||
| Line 60: | Line 53: | ||
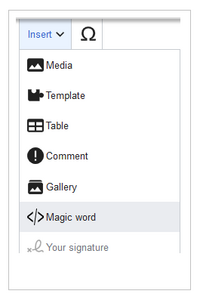
Magic words are inserted directly in the source code. Some frequently used Magic words can also be added directly with the VisualEditor ''Insert > Magic word'' menu item: | Magic words are inserted directly in the source code. Some frequently used Magic words can also be added directly with the VisualEditor ''Insert > Magic word'' menu item: | ||
[[File:Manual:VE-insert-magicword.png | [[File:VE-insert-magicword.png|300x300px|link=Special:FilePath/Manual:VE-insert-magicword.png]] | ||
{{Box Links-en | {{Box Links-en | ||
|Topic1=[https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Help:Magic_words mediawiki.org/wiki/Help:Magic_words] | |Topic1=[https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Help:Magic_words mediawiki.org/wiki/Help:Magic_words] | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[Category:Editing]] | [[Category:Editing]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:40, 30 September 2022
A "Magic word" is a string of text that is recognized by the knowledge base. It triggers the software to return the value of a function, such as dates, website statistics or page names.
4.1 Types of Magic words
There are basically four different types of Magic words:
- Behavior switch (or "Double underscore"):
__TOC__ - Variable:
{{FULLPAGENAME}} - Tag:
<gallery> - Parser function:
{{#ifeq:x|y|true|false}}
4.1.1 Behavior switch
Characteristics of a behavior switch
- Purpose: controls the layout or behavior of the page
- Syntax:
__NOTOC__
Description
A behavior switch includes or omits certain elements of the page. It is also known as "double underscore". Behavior switches can be put anywhere in the source code of the designated page (usually at the end of the page). The behavior switch __TOC__ produces as output the table of contents exactly where it was inserted on the page.
4.1.2 Variable
Characteristics of a variable
- Purpose: returns information about the page, wiki, or date
- Syntax:
{{PAGENAME}}
Description
Variables contain (simple) dynamic data. If a template name conflicts with a variable, the variable is used. For example, you have the variable {{PAGENAME}}. In that case, you have to transclude the template with the same name as {{Template:PAGENAME}}.
4.1.3 Tag
Characteristics of a tag
- Purpose: often used for custom development to process dynamic content
- Syntax:
<smartlist />
Description
Tags are implemented in PHP as part of a MediaWiki extension.
4.1.4 Parser Function
Characteristics of a parser function
- Purpose: simple "programming language" for page content (mainly in templates)
- Syntax:
{{#if:{{{field|}}} | {{{field|}}} | N/A }}
Description
Parser functions are similar to variables, but take one or more parameters.Example:
{{#ifeq:{{{type}}}|warning
|This is a warning!
|
}}
They are used for simple logic only, since they are hard to read and to maintain on a larger scale. If complex logic is required, consider Lua scripts in the "Module" namespace (mediawiki.org/wiki/Extension:Scribunto) and invoke using {{#invoke:...}}
Parser functions can also be "tag-like", e.g. {{#ask:...}} from SemanticMediaWiki. For more information, refer to the MediaWiki help pages mediawiki.org/wiki/Help:Extension:ParserFunctions and mediawiki.org/wiki/Help:Magic_words#Parser_functions.
4.1.5 Adding a Magic word
Magic words are inserted directly in the source code. Some frequently used Magic words can also be added directly with the VisualEditor Insert > Magic word menu item: